L4M1 Exam Question 1
Describe what is meant by the 5 Rights of Procurement (25 points)
Correct Answer:
See the solution inExplanation partbelow.
Explanation:
How to approach the question
- This question is worth 25 marks so you can imagine what the mark scheme will look like. There are 5 Rights so there will be 5 points for each Right. Naming the Right will be one point, then you have 4 points for a description and example. You should therefore aim to have 4-5 sentences per Right.
- I would recommend using headings for this type of essay- clearly putting your essay into 5 sections for each right. This makes it easy for the examiner to mark.
Proposed Essay structure
- Introduction - what is meant by the 5 Rights
- Price
- Quality
- Quantity
- Time
- Place
- Conclusion - why it's important, all rights are equally as important
Example Essay
Procurement revolves around achieving the delicate balance of acquiring goods and/ or services at the right price, quality, quantity, time, and place. This essay explains why these "Five Rights of Procurement" are important and explains how using this metric can help procurement to make smart choices when they purchase goods or services.
Price:
Firstly, it is important that procurement do not simply seek to find the cheapest option. The First Right is about finding the product/ service at an affordable price that doesn't compromise on quality. Let's say a company is buying office furniture. They might go for a supplier that offers a good balance between cost and quality, ensuring they get good value for their money. Considerations here may include Total Cost of Ownership, the Price Iceberg, and Whole Life Costing. The company therefore may seek to get the best price, but in relation to how long the furniture will last. A cheap chair that will break after one year may not be the best price compared to another chair which will last 10 years.
Quality:
The second right, quality, looks at legal compliance and fitness for purpose. Quality adherence aligns with specifications as well as legislation such as the UK Sale of Goods Act 1979. This helps ensure that items meet their commonly intended purpose and maintains satisfactory condition. Buyers deploy both reactive measures like Quality Control and proactive approaches like Quality Assurance to uphold the stipulated quality. This commitment not only ensures legal compliance but also underpins customer satisfaction, brand reputation, and ethical sourcing policies. An example of quality is an organisation buying a washing machine that conforms to ISO standard 97.060 and has a 2-year warrantee.
Quantity:
The third right, quantity, is a strategic consideration about how much of an item to order. It is connected to efficient inventory management. One tool that procurement can use to ensure they order the right quantity of a product is Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) - this serves as a tool for finding the equilibrium between stock-holding costs and avoiding stockouts. Market conditions, supply chain dynamics (e.g. JIT / Lean manufacturing), and organizational policies collectively play a pivotal role in determining the right quantity. For example a confectionary manufacturer will need to order the right number of eggs to make cakes- they will need to consider how many eggs they will need in order to make the cakes, but also take into consideration that they may not need them all at onceand that eggs can expire. The use of an MRP system is helpful when determining quantities of products to order.
Time:
Time is about getting things when we need them. In the above example, an egg delivery timing for a confectionary manufacturer will be pivotal to making the cakes on time. Other considerations about time include changing market forces and customer demand. The use of forecasting is therefore extremely useful; particularly if there are peaks in demand for a product, such as toys at Christmas.
Moreover, organizations need to avoid bottlenecks and production stoppages, so time (including lead time and delivery time) is an important consideration when making orders.
Place:
Lastly, place is about getting things to the right location. Minimizing environmental impact, reducing risks during transit, and optimizing warehousing practices contribute to achieving the right place. This is particularly important for perishable items such as food, and for items which require specific storage conditions such as chemicals. This involves good planning in terms of logistics, minimizing any impact on the environment during transport and a consideration for safety.
In conclusion, the Five Rights of Procurement provide a structured framework for organizations to optimize their sourcing practices. All rights are equally as important and it is the relationship between the Rights which is key. While price, quality, quantity, time, and place form the foundation, evolving models acknowledge additional elements like the Right Relationship with the Supplier. Embracing these principles not only ensures operational efficiency but also promotes sustainability and ethical conduct throughout the procurement process, contributing to long-term success in a globalized and dynamic marketplace.
Tutor Notes
- The 5 Rights is a big topic in CIPS so do learn them off by heart. It's p. 20 in the study guide.
- The conclusion mentions that additional 'rights' are starting to be introduced into the matrix, this is true and isn't mentioned in this study guide. I believe this starts to come up in Level 5. Just something to be aware of- some people are now talking about other Rights such as finding the right supplier and the right relationship. It's good to know, but not essential for this essay. Neither is knowing the ISO standard for washing machines - that's certainly not in the book. You can sprinkle in your own knowledge to essays like this, as it demonstrates you're able to apply the theory to real life. Why I remember the ISO for washing machines is a different story....
- You could also have mentioned the following topics;
o price - using the right currency and incoterm, aggregation of spend, negotiating prices o quality - conformance and performance specs o quantity - fulfilling retail orders, large order quantities leading to discount o time - additional costs of a stockout, impact on relationships and reputation o place - additional costs if delivery fails
- This is the type of question you can easily over-write. It's a huge topic and you could easily spend too long on it and not have enough time to answer other questions. So be careful with your timings. You don't need to mention everything above.
- Another way this type of question can come up is as a scenario. E.g. XYZ is a manufacturer of cakes and needs to order eggs. Discuss how XYZ can ensure the 5 Rights of Procurement when ordering Eggs.
Explanation:
How to approach the question
- This question is worth 25 marks so you can imagine what the mark scheme will look like. There are 5 Rights so there will be 5 points for each Right. Naming the Right will be one point, then you have 4 points for a description and example. You should therefore aim to have 4-5 sentences per Right.
- I would recommend using headings for this type of essay- clearly putting your essay into 5 sections for each right. This makes it easy for the examiner to mark.
Proposed Essay structure
- Introduction - what is meant by the 5 Rights
- Price
- Quality
- Quantity
- Time
- Place
- Conclusion - why it's important, all rights are equally as important
Example Essay
Procurement revolves around achieving the delicate balance of acquiring goods and/ or services at the right price, quality, quantity, time, and place. This essay explains why these "Five Rights of Procurement" are important and explains how using this metric can help procurement to make smart choices when they purchase goods or services.
Price:
Firstly, it is important that procurement do not simply seek to find the cheapest option. The First Right is about finding the product/ service at an affordable price that doesn't compromise on quality. Let's say a company is buying office furniture. They might go for a supplier that offers a good balance between cost and quality, ensuring they get good value for their money. Considerations here may include Total Cost of Ownership, the Price Iceberg, and Whole Life Costing. The company therefore may seek to get the best price, but in relation to how long the furniture will last. A cheap chair that will break after one year may not be the best price compared to another chair which will last 10 years.
Quality:
The second right, quality, looks at legal compliance and fitness for purpose. Quality adherence aligns with specifications as well as legislation such as the UK Sale of Goods Act 1979. This helps ensure that items meet their commonly intended purpose and maintains satisfactory condition. Buyers deploy both reactive measures like Quality Control and proactive approaches like Quality Assurance to uphold the stipulated quality. This commitment not only ensures legal compliance but also underpins customer satisfaction, brand reputation, and ethical sourcing policies. An example of quality is an organisation buying a washing machine that conforms to ISO standard 97.060 and has a 2-year warrantee.
Quantity:
The third right, quantity, is a strategic consideration about how much of an item to order. It is connected to efficient inventory management. One tool that procurement can use to ensure they order the right quantity of a product is Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) - this serves as a tool for finding the equilibrium between stock-holding costs and avoiding stockouts. Market conditions, supply chain dynamics (e.g. JIT / Lean manufacturing), and organizational policies collectively play a pivotal role in determining the right quantity. For example a confectionary manufacturer will need to order the right number of eggs to make cakes- they will need to consider how many eggs they will need in order to make the cakes, but also take into consideration that they may not need them all at onceand that eggs can expire. The use of an MRP system is helpful when determining quantities of products to order.
Time:
Time is about getting things when we need them. In the above example, an egg delivery timing for a confectionary manufacturer will be pivotal to making the cakes on time. Other considerations about time include changing market forces and customer demand. The use of forecasting is therefore extremely useful; particularly if there are peaks in demand for a product, such as toys at Christmas.
Moreover, organizations need to avoid bottlenecks and production stoppages, so time (including lead time and delivery time) is an important consideration when making orders.
Place:
Lastly, place is about getting things to the right location. Minimizing environmental impact, reducing risks during transit, and optimizing warehousing practices contribute to achieving the right place. This is particularly important for perishable items such as food, and for items which require specific storage conditions such as chemicals. This involves good planning in terms of logistics, minimizing any impact on the environment during transport and a consideration for safety.
In conclusion, the Five Rights of Procurement provide a structured framework for organizations to optimize their sourcing practices. All rights are equally as important and it is the relationship between the Rights which is key. While price, quality, quantity, time, and place form the foundation, evolving models acknowledge additional elements like the Right Relationship with the Supplier. Embracing these principles not only ensures operational efficiency but also promotes sustainability and ethical conduct throughout the procurement process, contributing to long-term success in a globalized and dynamic marketplace.
Tutor Notes
- The 5 Rights is a big topic in CIPS so do learn them off by heart. It's p. 20 in the study guide.
- The conclusion mentions that additional 'rights' are starting to be introduced into the matrix, this is true and isn't mentioned in this study guide. I believe this starts to come up in Level 5. Just something to be aware of- some people are now talking about other Rights such as finding the right supplier and the right relationship. It's good to know, but not essential for this essay. Neither is knowing the ISO standard for washing machines - that's certainly not in the book. You can sprinkle in your own knowledge to essays like this, as it demonstrates you're able to apply the theory to real life. Why I remember the ISO for washing machines is a different story....
- You could also have mentioned the following topics;
o price - using the right currency and incoterm, aggregation of spend, negotiating prices o quality - conformance and performance specs o quantity - fulfilling retail orders, large order quantities leading to discount o time - additional costs of a stockout, impact on relationships and reputation o place - additional costs if delivery fails
- This is the type of question you can easily over-write. It's a huge topic and you could easily spend too long on it and not have enough time to answer other questions. So be careful with your timings. You don't need to mention everything above.
- Another way this type of question can come up is as a scenario. E.g. XYZ is a manufacturer of cakes and needs to order eggs. Discuss how XYZ can ensure the 5 Rights of Procurement when ordering Eggs.
L4M1 Exam Question 2
Describe the main characteristics of, and differences between, procuring goods, services and construction works (25 points)
Correct Answer:
See the solution inExplanation partbelow.
Explanation:
- there are a lot of components to this question so I would take a good 5 minutes to write out some bullet points on the characteristics of each one, and on some differences. Then from your notes make this into an essay. The mark scheme isn't 100% clear on how many characteristics and differences you need to name, so try and keep an equal split between the two areas. You would probably need 2-3 characteristics of each, and 3 differences for a good score.
- Characteristics of goods: tangible, homogeneous, items tend not to perish quickly, can be stored
- Characteristics of services: intangible, heterogenous, inseparable (produced and consumed at the same time), no transfer of ownership, perish upon use (i.e. cannot be stored)
- Characteristics of construction work: project-based procurement, includes procuring both goods and services, complex procurement which has its own set of regulations (CDM2015).
- Differences between these
1) goods are not usually outsourced and services can be.
2) Complexity of the supply chain (goods and construction may have a complex supply chains, but service contracts usually only involve 2 parties).
3) Timescales - construction work has a designated timescale but procurement of goods could be a one off or long-term contract, services is usually a long-term contract.
Example Essay
Introduction:
Procurement is a multifaceted field, and understanding the nuances between procuring goods, services, and construction works is pivotal for effective management. This essay explores the main characteristics that differentiate these categories.
Tangible / Intangible:
Goods are tangible items that can be physically seen and touched. For instance, raw materials like wheat and sugar in a manufacturing organization are tangible goods. On the other hand, services are intangible-though the results can be observed, the service itself cannot be touched. An example is a cleaning contract for a factory; while the effects of the cleaning are visible, the service itself remains intangible. Construction is usually a mixture of tangible and intangible procurement; the tangible is the construction materials such as bricks and windows, and the intangible aspect is the labour to complete the project.
Heterogeneous / Homogeneous:
Goods are generally homogeneous, meaning they are always the same. For example, steel purchased for manufacturing purposes will always be the same. In contrast, services areheterogeneous, varying each time they are rendered. Customer service, for instance, is inherently different each time due to the dynamic nature of customer interactions. Construction could be either heterogeneous or homogeneous depending on the project - is it a one off unique building, or is it a large housing estate of same-build properties?
Transfer of Ownership:
When goods are procured, there is a transfer of ownership. The product becomes the property of the buyer upon delivery and payment. In contrast, services do not involve a transfer of ownership as there is no physical entity to transfer. In construction the transfer of ownership is extremely complex and varies depending on the project. Usually the buyer will retain ownership of the land throughout the project, but on some occasions the construction company may take ownership for insurance purposes.
Storable (Separable/ Inseparable):
Goods are storable, allowing for purchase on one day and use on another. For example a factory can buy in plastic to be used to manufacture toys and this is stored in inventory until the time comes to make the toys.
However, services are consumed at the point of purchase, making them inseparable. The service is bought and utilized simultaneously. Services cannot be stored. This is the same for construction.
Ability to Outsource:
Goods are rarely outsourced, as they are typically purchased directly from suppliers. Services, on the other hand, can be easily outsourced-examples include outsourcing finance, cleaning, or security services.
Construction works are commonly outsourced, with external companies hired to execute projects.
Complexity of the Supply Chain:
Service contracts often involve a simple two-party relationship between the buyer and the supplier. Goods and construction, however, may have complex supply chains. For example, procuring a pen involves a supply chain with various steps, including the raw material supplier, manufacturer, and possibly a wholesaler.
Construction works often feature a tiered supply chain with subcontractors playing crucial roles.
Construction as a Hybrid:
Construction procurement represents a hybrid, incorporating elements of both goods and services. It involves hiring a service, such as a bricklayer for laying bricks, while also procuring the tangible goods-bricks.
Separating goods from services in construction is challenging, as they are often intertwined, and both aspects are paid for simultaneously.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, distinguishing between the procurement of goods, services, and construction works is essential for effective supply chain management. The tangible or intangible nature, heterogeneity, transfer of ownership, storability, outsourcing potential, and supply chain complexities offer a comprehensive framework for understanding the unique characteristics of each category. Recognizing these distinctions empowers organizations to tailor their procurement strategies to the specific challenges and dynamics associated with goods, services, and construction works.
Tutor Notes
- What a characteristic is can also be a difference. So for example you can say tangible is a characteristic of goods but tangibility is also the main difference between goods and services. So don't worry too much about which order to write stuff in, or doing clear sections for this type of essay. It all comes out in the wash.
- Other differences in procuring these include:
- Costs: procuring goods such as stationary for an office will be low-cost so may not require approval, but a service contract may require management sign off. Procuring construction projects tend to be huge sums of money
- Where the budget comes from: goods and services may be operational expenditure and construction works capital expenditure.
- The level of risk involved in the procurement: goods tends to be quite low risk and construction high risk.
- Types of contract involved: procuring goods may be very simple and just require a PO, services is more complex so may require a formal contract or Deed of Appointment. Construction projects will require a contract due to the high value and high risk of the purchase
- Legislation - Goods = Sale of Goods Act, Construction - CDM Regulations 2015. Construction is much more heavily regulated than services or goods. Note CDM regulations isn't part of CIPS. It's occasionally referenced in various modules but you don't have to really know what it is. Just know it's the main legislation governing the construction industry. Construction - Construction Design and Management Regulations 2015 (hse.gov.uk)
- Study guide LO 1.3.1 p. 40, but mainly p. 52 for services. NOTE the title of this learning outcome includes construction and it is hardly mentioned in the study guide. Most of the above information on construction comes from my own knowledge rather than the book.
Explanation:
- there are a lot of components to this question so I would take a good 5 minutes to write out some bullet points on the characteristics of each one, and on some differences. Then from your notes make this into an essay. The mark scheme isn't 100% clear on how many characteristics and differences you need to name, so try and keep an equal split between the two areas. You would probably need 2-3 characteristics of each, and 3 differences for a good score.
- Characteristics of goods: tangible, homogeneous, items tend not to perish quickly, can be stored
- Characteristics of services: intangible, heterogenous, inseparable (produced and consumed at the same time), no transfer of ownership, perish upon use (i.e. cannot be stored)
- Characteristics of construction work: project-based procurement, includes procuring both goods and services, complex procurement which has its own set of regulations (CDM2015).
- Differences between these
1) goods are not usually outsourced and services can be.
2) Complexity of the supply chain (goods and construction may have a complex supply chains, but service contracts usually only involve 2 parties).
3) Timescales - construction work has a designated timescale but procurement of goods could be a one off or long-term contract, services is usually a long-term contract.
Example Essay
Introduction:
Procurement is a multifaceted field, and understanding the nuances between procuring goods, services, and construction works is pivotal for effective management. This essay explores the main characteristics that differentiate these categories.
Tangible / Intangible:
Goods are tangible items that can be physically seen and touched. For instance, raw materials like wheat and sugar in a manufacturing organization are tangible goods. On the other hand, services are intangible-though the results can be observed, the service itself cannot be touched. An example is a cleaning contract for a factory; while the effects of the cleaning are visible, the service itself remains intangible. Construction is usually a mixture of tangible and intangible procurement; the tangible is the construction materials such as bricks and windows, and the intangible aspect is the labour to complete the project.
Heterogeneous / Homogeneous:
Goods are generally homogeneous, meaning they are always the same. For example, steel purchased for manufacturing purposes will always be the same. In contrast, services areheterogeneous, varying each time they are rendered. Customer service, for instance, is inherently different each time due to the dynamic nature of customer interactions. Construction could be either heterogeneous or homogeneous depending on the project - is it a one off unique building, or is it a large housing estate of same-build properties?
Transfer of Ownership:
When goods are procured, there is a transfer of ownership. The product becomes the property of the buyer upon delivery and payment. In contrast, services do not involve a transfer of ownership as there is no physical entity to transfer. In construction the transfer of ownership is extremely complex and varies depending on the project. Usually the buyer will retain ownership of the land throughout the project, but on some occasions the construction company may take ownership for insurance purposes.
Storable (Separable/ Inseparable):
Goods are storable, allowing for purchase on one day and use on another. For example a factory can buy in plastic to be used to manufacture toys and this is stored in inventory until the time comes to make the toys.
However, services are consumed at the point of purchase, making them inseparable. The service is bought and utilized simultaneously. Services cannot be stored. This is the same for construction.
Ability to Outsource:
Goods are rarely outsourced, as they are typically purchased directly from suppliers. Services, on the other hand, can be easily outsourced-examples include outsourcing finance, cleaning, or security services.
Construction works are commonly outsourced, with external companies hired to execute projects.
Complexity of the Supply Chain:
Service contracts often involve a simple two-party relationship between the buyer and the supplier. Goods and construction, however, may have complex supply chains. For example, procuring a pen involves a supply chain with various steps, including the raw material supplier, manufacturer, and possibly a wholesaler.
Construction works often feature a tiered supply chain with subcontractors playing crucial roles.
Construction as a Hybrid:
Construction procurement represents a hybrid, incorporating elements of both goods and services. It involves hiring a service, such as a bricklayer for laying bricks, while also procuring the tangible goods-bricks.
Separating goods from services in construction is challenging, as they are often intertwined, and both aspects are paid for simultaneously.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, distinguishing between the procurement of goods, services, and construction works is essential for effective supply chain management. The tangible or intangible nature, heterogeneity, transfer of ownership, storability, outsourcing potential, and supply chain complexities offer a comprehensive framework for understanding the unique characteristics of each category. Recognizing these distinctions empowers organizations to tailor their procurement strategies to the specific challenges and dynamics associated with goods, services, and construction works.
Tutor Notes
- What a characteristic is can also be a difference. So for example you can say tangible is a characteristic of goods but tangibility is also the main difference between goods and services. So don't worry too much about which order to write stuff in, or doing clear sections for this type of essay. It all comes out in the wash.
- Other differences in procuring these include:
- Costs: procuring goods such as stationary for an office will be low-cost so may not require approval, but a service contract may require management sign off. Procuring construction projects tend to be huge sums of money
- Where the budget comes from: goods and services may be operational expenditure and construction works capital expenditure.
- The level of risk involved in the procurement: goods tends to be quite low risk and construction high risk.
- Types of contract involved: procuring goods may be very simple and just require a PO, services is more complex so may require a formal contract or Deed of Appointment. Construction projects will require a contract due to the high value and high risk of the purchase
- Legislation - Goods = Sale of Goods Act, Construction - CDM Regulations 2015. Construction is much more heavily regulated than services or goods. Note CDM regulations isn't part of CIPS. It's occasionally referenced in various modules but you don't have to really know what it is. Just know it's the main legislation governing the construction industry. Construction - Construction Design and Management Regulations 2015 (hse.gov.uk)
- Study guide LO 1.3.1 p. 40, but mainly p. 52 for services. NOTE the title of this learning outcome includes construction and it is hardly mentioned in the study guide. Most of the above information on construction comes from my own knowledge rather than the book.
L4M1 Exam Question 3
Explain, with examples, the three different ways one can categorise procurement spend: direct vs indirect, capital expenditure vs operational expenditure and stock vs non-stock items. (25 points)
Correct Answer:
See the solution inExplanation partbelow.
Explanation:
The knowledge to remember:
A table with text on it Description automatically generated
Essay Plan :
Remember to include examples for each of the six categories of spend. This is specifically asked for in the question so it's important to include as many examples as you can. To do this you could take an example organisation such as a cake manufacturer and explain which of their purchases would fall into each category and why.
Introduction - explain why procurement categorises spend
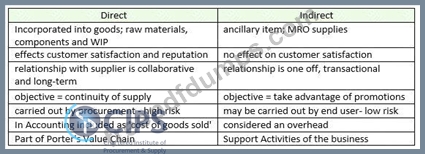
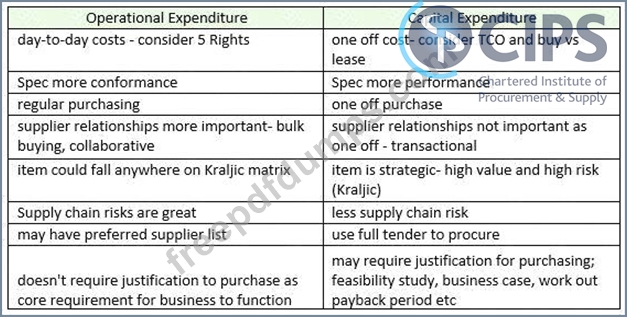
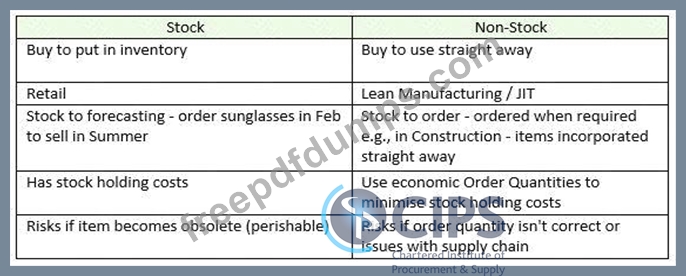
- Direct - these are items that are incorporated into the final goods (the cakes) so would include raw materials such as flour, eggs, sugar etc
- Indirect - these are items that the company needs, but don't go into the end product. For example, cleaning products and MRO supplies for the machines
- Capital Expenditure- these are large one-off purchases, such as buying a new piece of equipment such as a giant oven to cook the cakes.
- Operational Expenditure - these are purchases that are required to ensure the business can function day-to-day. They may include PPE for the workers in the factory and cleaning equipment
- Stock items - these are items procured in advance and held in inventory until they are needed. In a cake manufacturing factory this could be PPE for staff such as hairnets and gloves. The organisation will buy these in bulk and keep them in a stock cupboard, using these as and when they are required
- Non- stock items - items that are not stored and used right away. An example would be eggs- these will need to be put directly into the cakes as they would go off if bought in advance.
Conclusion - the categories are not mutually exclusive - an item can be direct and operational, or indirect and stock. Different companies may use different systems to classify items of spend.
Example Introduction and Conclusion
Introduction
Procurement categorizes spend to efficiently manage resources and make strategic decisions. Three primary ways of categorizing procurement spend include distinguishing between direct and indirect spend, classifying expenditures as capital or operational, and categorizing items as stock or non-stock. These distinctions aid organizations in optimizing their procurement strategies for better resource allocation.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, categorizing procurement spend into direct vs. indirect, capital vs. operational, and stock vs.
non-stock items is essential for strategic resource management. While these categories provide a structured framework, they are not mutually exclusive, as an item can fall into multiple categories. For example, an item may be both direct and operational or indirect and stock. The flexibility of these categories allows organizations to tailor their procurement strategies based on their specific needs, ensuring efficient resource allocation and effective supply chain management. Different companies may adopt varying categorization approaches depending on their industry, size, and operational requirements.
Tutor notes:
- Because you've got 6 categories of spend to talk about you're only going to need 3-4 sentences for each.
Providing you've said the category, explained what it is and given one example, you'll absolutely fly through this type of question
- You could also mention that it is useful to use categories of spend as this helps with budgeting. Different categories may also have different processes to follow for procuring the item (this could form part of your introduction or conclusion).
- This subject is LO 1.3.2 it's quite spread out in the text book but the main info is on p.49
- Note- different companies/ industries classify items of spend differently. Particularly packaging and salaries.
Some say they're direct costs and some say they're indirect costs. Honestly, it's a hotly debated subject and I don't think there is a right or wrong. I'd just avoid those two examples if you can and stick to ones that aren't as contentious like eggs and PPE.
Explanation:
The knowledge to remember:
A table with text on it Description automatically generated



Essay Plan :
Remember to include examples for each of the six categories of spend. This is specifically asked for in the question so it's important to include as many examples as you can. To do this you could take an example organisation such as a cake manufacturer and explain which of their purchases would fall into each category and why.
Introduction - explain why procurement categorises spend
- Direct - these are items that are incorporated into the final goods (the cakes) so would include raw materials such as flour, eggs, sugar etc
- Indirect - these are items that the company needs, but don't go into the end product. For example, cleaning products and MRO supplies for the machines
- Capital Expenditure- these are large one-off purchases, such as buying a new piece of equipment such as a giant oven to cook the cakes.
- Operational Expenditure - these are purchases that are required to ensure the business can function day-to-day. They may include PPE for the workers in the factory and cleaning equipment
- Stock items - these are items procured in advance and held in inventory until they are needed. In a cake manufacturing factory this could be PPE for staff such as hairnets and gloves. The organisation will buy these in bulk and keep them in a stock cupboard, using these as and when they are required
- Non- stock items - items that are not stored and used right away. An example would be eggs- these will need to be put directly into the cakes as they would go off if bought in advance.
Conclusion - the categories are not mutually exclusive - an item can be direct and operational, or indirect and stock. Different companies may use different systems to classify items of spend.
Example Introduction and Conclusion
Introduction
Procurement categorizes spend to efficiently manage resources and make strategic decisions. Three primary ways of categorizing procurement spend include distinguishing between direct and indirect spend, classifying expenditures as capital or operational, and categorizing items as stock or non-stock. These distinctions aid organizations in optimizing their procurement strategies for better resource allocation.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, categorizing procurement spend into direct vs. indirect, capital vs. operational, and stock vs.
non-stock items is essential for strategic resource management. While these categories provide a structured framework, they are not mutually exclusive, as an item can fall into multiple categories. For example, an item may be both direct and operational or indirect and stock. The flexibility of these categories allows organizations to tailor their procurement strategies based on their specific needs, ensuring efficient resource allocation and effective supply chain management. Different companies may adopt varying categorization approaches depending on their industry, size, and operational requirements.
Tutor notes:
- Because you've got 6 categories of spend to talk about you're only going to need 3-4 sentences for each.
Providing you've said the category, explained what it is and given one example, you'll absolutely fly through this type of question
- You could also mention that it is useful to use categories of spend as this helps with budgeting. Different categories may also have different processes to follow for procuring the item (this could form part of your introduction or conclusion).
- This subject is LO 1.3.2 it's quite spread out in the text book but the main info is on p.49
- Note- different companies/ industries classify items of spend differently. Particularly packaging and salaries.
Some say they're direct costs and some say they're indirect costs. Honestly, it's a hotly debated subject and I don't think there is a right or wrong. I'd just avoid those two examples if you can and stick to ones that aren't as contentious like eggs and PPE.
L4M1 Exam Question 4
Mo is the new Head of Procurement at Manufacturer X. Manufacturer X is a small organisation which creates bespoke robots for clients. Their supply chain is complex, sourcing many components from various suppliers.
Mo has joined the company at a pivotal time of growth. The company wishes to expand the procurement department and formalise its policies. Discuss 5 areas that Mo should consider when drafting the department's policies and manuals (25 points).
Mo has joined the company at a pivotal time of growth. The company wishes to expand the procurement department and formalise its policies. Discuss 5 areas that Mo should consider when drafting the department's policies and manuals (25 points).
Correct Answer:
See the solution inExplanation partbelow.
Explanation:
How to approach this question
- Remember as you're preparing an essay plan that this is a case study question, meaning everything has to relate back to Mo and Manufacturer X. So for the 5 areas- think about how this would be applicable for a robotics manufacturer. CIPS don't expect you to knowanything about robotics so if you talk about KPIs for suppliers- just make them up- as long as they sound right-ish that's all that matters.
- Areas you could talk about include: competition, ethics, KPIs, quality, supplier appraisal, supplier evaluation, sustainability, transparency Example Essay Mo, stepping into the role of Head of Procurement at Manufacturer X during a pivotal period of growth, faces the task of expanding the department and formalizing its policies. In this intricate landscape of a small organization creating bespoke robots, five crucial areas demand Mo's careful consideration in the drafting of departmental policies and manuals: competition, ethics, quality, supplier evaluation, and sustainability.
Firstly, competition. As Manufacturer X navigates growth, Mo must establish transparent guidelines for competitive bidding processes. It is imperative to ensure fairness in supplier selection and implement strategies for cost competitiveness without compromising quality. Encouraging innovation and collaboration with suppliers becomes a strategic approach to gain a competitive edge in the market. Mo should be careful that his policies do not favour any suppliers over others and that consideration is given to allowing SMEs to bid for work.
Secondly, Ethics. Mo needs to develop an explicit code of ethics guiding procurement professionals in their interactions. This should emphasize honesty, integrity, and fair treatment. Additionally, establishing due diligence procedures to ensure suppliers adhere to ethical business practices, especially concerning labour and environmental standards is important. Moreover, whistleblower protection mechanisms should be put in place to encourage the reporting of ethical concerns without fear of reprisal.
Thirdly, Quality considerations. Given the bespoke nature of the robotics industry and the necessity of maintaining high standards for customer satisfaction, Mo must define and communicate stringent quality requirements to suppliers, emphasizing adherence to specifications and standards. The establishment of robust inspection and testing procedures at various stages of the supply chain is crucial, ensuring consistent component quality. Developing contingency plans and protocols for addressing quality issues promptly, including collaboration with suppliers for continuous improvement, should be integrated.
With the organization's growth, a systematic approach to supplier evaluation becomes paramount. Mo needs to develop a comprehensive evaluation framework, including criteria such as financial stability, reliability, and past performance. Implementing a supplier scorecard system is essential for tracking and assessing supplier performance over time. Moreover, fostering strategic relationships with key suppliers to promote collaboration, innovation, and long-term partnerships becomes a strategic imperative.
Lastly, Mo should consider sustainability, in particular environmental awareness and the promotion of sustainable practices into the supply chain for long-term viability. Developing sustainability criteria for supplier selection, considering factors such as environmental impact, social responsibility, and ethical sourcing, is imperative. Encouraging suppliers to adopt environmentally friendly practices and certifications, such as ISO14001 or Fair Trade, becomes crucial. The integration of sustainability goals into procurement key performance indicators (KPIs) is essential for tracking progress and demonstrating the organization's commitment to corporate responsibility.
In conclusion, Mo's strategic focus on competition, ethics, quality, supplier evaluation, and sustainability is pivotal in laying the foundation for a procurement department that not only supports Manufacturer X's growth, but also aligns with its values and industry standards.This approach positions the organization for success in the dynamic landscape of bespoke robot manufacturing.
Tutor Notes
- This question is taken from P. 146 - note the question is on policies not strategy. These are slightly different concepts, but they do overlap. Policies are black and white- we do this and we don't do that. Strategies are about what the company wants to achieve. They're future orientated, where as a policy is about what we do now. So a policy may include sustainability, but strategy may talk about reducing pollution.
- CIPS could also ask you to talk about procurement strategies such as achieving cost reductions, environmental issues etc. These are also on p.146
Explanation:
How to approach this question
- Remember as you're preparing an essay plan that this is a case study question, meaning everything has to relate back to Mo and Manufacturer X. So for the 5 areas- think about how this would be applicable for a robotics manufacturer. CIPS don't expect you to knowanything about robotics so if you talk about KPIs for suppliers- just make them up- as long as they sound right-ish that's all that matters.
- Areas you could talk about include: competition, ethics, KPIs, quality, supplier appraisal, supplier evaluation, sustainability, transparency Example Essay Mo, stepping into the role of Head of Procurement at Manufacturer X during a pivotal period of growth, faces the task of expanding the department and formalizing its policies. In this intricate landscape of a small organization creating bespoke robots, five crucial areas demand Mo's careful consideration in the drafting of departmental policies and manuals: competition, ethics, quality, supplier evaluation, and sustainability.
Firstly, competition. As Manufacturer X navigates growth, Mo must establish transparent guidelines for competitive bidding processes. It is imperative to ensure fairness in supplier selection and implement strategies for cost competitiveness without compromising quality. Encouraging innovation and collaboration with suppliers becomes a strategic approach to gain a competitive edge in the market. Mo should be careful that his policies do not favour any suppliers over others and that consideration is given to allowing SMEs to bid for work.
Secondly, Ethics. Mo needs to develop an explicit code of ethics guiding procurement professionals in their interactions. This should emphasize honesty, integrity, and fair treatment. Additionally, establishing due diligence procedures to ensure suppliers adhere to ethical business practices, especially concerning labour and environmental standards is important. Moreover, whistleblower protection mechanisms should be put in place to encourage the reporting of ethical concerns without fear of reprisal.
Thirdly, Quality considerations. Given the bespoke nature of the robotics industry and the necessity of maintaining high standards for customer satisfaction, Mo must define and communicate stringent quality requirements to suppliers, emphasizing adherence to specifications and standards. The establishment of robust inspection and testing procedures at various stages of the supply chain is crucial, ensuring consistent component quality. Developing contingency plans and protocols for addressing quality issues promptly, including collaboration with suppliers for continuous improvement, should be integrated.
With the organization's growth, a systematic approach to supplier evaluation becomes paramount. Mo needs to develop a comprehensive evaluation framework, including criteria such as financial stability, reliability, and past performance. Implementing a supplier scorecard system is essential for tracking and assessing supplier performance over time. Moreover, fostering strategic relationships with key suppliers to promote collaboration, innovation, and long-term partnerships becomes a strategic imperative.
Lastly, Mo should consider sustainability, in particular environmental awareness and the promotion of sustainable practices into the supply chain for long-term viability. Developing sustainability criteria for supplier selection, considering factors such as environmental impact, social responsibility, and ethical sourcing, is imperative. Encouraging suppliers to adopt environmentally friendly practices and certifications, such as ISO14001 or Fair Trade, becomes crucial. The integration of sustainability goals into procurement key performance indicators (KPIs) is essential for tracking progress and demonstrating the organization's commitment to corporate responsibility.
In conclusion, Mo's strategic focus on competition, ethics, quality, supplier evaluation, and sustainability is pivotal in laying the foundation for a procurement department that not only supports Manufacturer X's growth, but also aligns with its values and industry standards.This approach positions the organization for success in the dynamic landscape of bespoke robot manufacturing.
Tutor Notes
- This question is taken from P. 146 - note the question is on policies not strategy. These are slightly different concepts, but they do overlap. Policies are black and white- we do this and we don't do that. Strategies are about what the company wants to achieve. They're future orientated, where as a policy is about what we do now. So a policy may include sustainability, but strategy may talk about reducing pollution.
- CIPS could also ask you to talk about procurement strategies such as achieving cost reductions, environmental issues etc. These are also on p.146
L4M1 Exam Question 5
Explain what is meant by added value (5 points). Describe 4 ways the Procurement Department can add value for their organisation (20 points)
Correct Answer:
See the solution inExplanation partbelow.
Explanation:
What to include in the essay:
- Definition of added value: the economic enhancement given to products or services before offering them to customers. Examples may include a product which has additional features at no additional cost to the customer or the provision of an extended warrantee.
- Description of four of the following with examples andExplanation:s: providing better customer service levels, risk management, cost control and reduction, relationship management, reputation management, innovation, use of technology, streamlining processes, improving specifications, increasing sustainability, improving quality, ordering processes such as bulk ordering, inventory management, improving the product from the customer's perspective (e.g. packaging, exclusivity), sustainability, convenience, market development.
Example essay:
Added value in procurement refers to the enhancement or improvement in the economic worth, quality, or utility of products or services before they are offered to customers or end-users. In the context of procurement, the goal is to go beyond simply obtaining goods or services at the lowest cost. Instead, procurement aims to contribute additional value to the organization through various means. This essay explores the concept of added value and outlines four ways the Procurement Department can contribute to organizational improvement.
Improving Specifications
Procurement can add value firstly by ensuring all critical items are procured against a specification, and secondly by improving and regularly updating those specifications. For example, the procurement department might be responsible for procuring light-bulbs for an office. Having an effective specification for this purchase (lightbulbs must meet X safety standard and Y environmental standard) would result in less maverick buying for the organisation and the procurement of a better-quality product. Furthermore, regularly updating specifications ensures that purchases are made against current safety standards and regulations (e.g. the use of low-energy lightbulbs). If procurement don't update specifications, then there is a risk that items are bought that don't meet the correct standards.
Added value in this regard could also therefore be considered the removal of risks of procuring the wrong item.
Stream-lining Processes
Procurement can add value by stream-lining processes such as requisitions and POs. This reduces the time it takes to procure an item, thus saving the company money. Another process that could be streamlined is the re-ordering process of regularly bought items. This could be automated when the stock levels reach a certain level. For example if an organisation requires its staff to wear PPE, an automatic request could be made once there are only 50 face masks left.
Managing Supplier Relationships
Having strong, positive relationships with suppliers is a source of added value as it means suppliers value you as a buyer and are therefore more likely to help in situations which are adversely affecting business. For example, if a manufacturer puts an order in for 300 items with their supplier but then realises that they have made an error in the amount, if there is a strong relationship, the supplier may allow the buyer to amend the order after the fact. If there is a poor relationship, the supplier may not be as flexible. The flexibility in the supply chain is therefore a source of added value.
Improving Quality / Innovation
This involves adding value from the customer's perspective. E.g. a customer may choose to purchase a phone that has a longer battery life than others. Procurement's role in this may be in completing a Value Engineering exercise or procuring higher quality components or materials at the same price in order to achieve this additional feature.
In conclusion, the Procurement Department plays a crucial role in organizational success by adding value through improved specifications, streamlined processes, strong supplier relationships, and a focus on quality and innovation. These strategies contribute to enhanced efficiency, reduced risks, and increased customer satisfaction, making procurement an essential function for organizational excellence.
Tutor Notes
- The question asks specifically to name 4 ways of adding value. You therefore won't get any additional points if you talk about 5 or 6, even though it may be tempting. Instead, focus your response on providing more information on the 4 you have chosen and bulking out your answer with examples. This demonstrates to the examiner that you fully understand the topic AND that you can apply the theory to real situations.
- You could use real-life examples from your own organisation/ experience or you could give a hypothetical situation such as a cake manufacturer. You could talk through how the procurement department at the cake manufacturer can add value by doing the four things in your essay: by amending the specification so the cakes are more tasty, by streamlining the process for ordering flour, by managing the relationship with the company that fixes the machines when they break down, and by introducing innovation such as using an e-procurement system to source raw materials and the benefits that these will bring to the organisation.
- Added value is part of the syllabus for Learning Outcome 1.2 starting from p.19 but I'm gonna be honest, I think the new study guide is a bit crap on this part of the syllabus. The section starts talking about the 5 rights of procurement and I think that makes things very confusing for students. The 5 rights and added value are linked subjects, but they're not the same. Getting the rights right, CAN lead to sources of added value, but added value is value that is IN ADDITION to what is expected. So, when you have a question on added value, focus on stuff that's listed under 1.1.4 'other sources of added value' on p.35 rather than talking about the 5 rights of procurement. My list at the top is more exhaustive than the one in the study guide.
- If you're looking to be really clever you can quote Michael Porter on 'what is added value?'. Michael Porter looks at this from a customer perspective - 'added value' refers to the addition of greater value (either by reducing the cost to produce it, or by adding something that customers are willing to pay more for). These could be; marketing / design, customer service, maintenance, delivery etc. This comes up at Level 5 / 6.
Explanation:
What to include in the essay:
- Definition of added value: the economic enhancement given to products or services before offering them to customers. Examples may include a product which has additional features at no additional cost to the customer or the provision of an extended warrantee.
- Description of four of the following with examples andExplanation:s: providing better customer service levels, risk management, cost control and reduction, relationship management, reputation management, innovation, use of technology, streamlining processes, improving specifications, increasing sustainability, improving quality, ordering processes such as bulk ordering, inventory management, improving the product from the customer's perspective (e.g. packaging, exclusivity), sustainability, convenience, market development.
Example essay:
Added value in procurement refers to the enhancement or improvement in the economic worth, quality, or utility of products or services before they are offered to customers or end-users. In the context of procurement, the goal is to go beyond simply obtaining goods or services at the lowest cost. Instead, procurement aims to contribute additional value to the organization through various means. This essay explores the concept of added value and outlines four ways the Procurement Department can contribute to organizational improvement.
Improving Specifications
Procurement can add value firstly by ensuring all critical items are procured against a specification, and secondly by improving and regularly updating those specifications. For example, the procurement department might be responsible for procuring light-bulbs for an office. Having an effective specification for this purchase (lightbulbs must meet X safety standard and Y environmental standard) would result in less maverick buying for the organisation and the procurement of a better-quality product. Furthermore, regularly updating specifications ensures that purchases are made against current safety standards and regulations (e.g. the use of low-energy lightbulbs). If procurement don't update specifications, then there is a risk that items are bought that don't meet the correct standards.
Added value in this regard could also therefore be considered the removal of risks of procuring the wrong item.
Stream-lining Processes
Procurement can add value by stream-lining processes such as requisitions and POs. This reduces the time it takes to procure an item, thus saving the company money. Another process that could be streamlined is the re-ordering process of regularly bought items. This could be automated when the stock levels reach a certain level. For example if an organisation requires its staff to wear PPE, an automatic request could be made once there are only 50 face masks left.
Managing Supplier Relationships
Having strong, positive relationships with suppliers is a source of added value as it means suppliers value you as a buyer and are therefore more likely to help in situations which are adversely affecting business. For example, if a manufacturer puts an order in for 300 items with their supplier but then realises that they have made an error in the amount, if there is a strong relationship, the supplier may allow the buyer to amend the order after the fact. If there is a poor relationship, the supplier may not be as flexible. The flexibility in the supply chain is therefore a source of added value.
Improving Quality / Innovation
This involves adding value from the customer's perspective. E.g. a customer may choose to purchase a phone that has a longer battery life than others. Procurement's role in this may be in completing a Value Engineering exercise or procuring higher quality components or materials at the same price in order to achieve this additional feature.
In conclusion, the Procurement Department plays a crucial role in organizational success by adding value through improved specifications, streamlined processes, strong supplier relationships, and a focus on quality and innovation. These strategies contribute to enhanced efficiency, reduced risks, and increased customer satisfaction, making procurement an essential function for organizational excellence.
Tutor Notes
- The question asks specifically to name 4 ways of adding value. You therefore won't get any additional points if you talk about 5 or 6, even though it may be tempting. Instead, focus your response on providing more information on the 4 you have chosen and bulking out your answer with examples. This demonstrates to the examiner that you fully understand the topic AND that you can apply the theory to real situations.
- You could use real-life examples from your own organisation/ experience or you could give a hypothetical situation such as a cake manufacturer. You could talk through how the procurement department at the cake manufacturer can add value by doing the four things in your essay: by amending the specification so the cakes are more tasty, by streamlining the process for ordering flour, by managing the relationship with the company that fixes the machines when they break down, and by introducing innovation such as using an e-procurement system to source raw materials and the benefits that these will bring to the organisation.
- Added value is part of the syllabus for Learning Outcome 1.2 starting from p.19 but I'm gonna be honest, I think the new study guide is a bit crap on this part of the syllabus. The section starts talking about the 5 rights of procurement and I think that makes things very confusing for students. The 5 rights and added value are linked subjects, but they're not the same. Getting the rights right, CAN lead to sources of added value, but added value is value that is IN ADDITION to what is expected. So, when you have a question on added value, focus on stuff that's listed under 1.1.4 'other sources of added value' on p.35 rather than talking about the 5 rights of procurement. My list at the top is more exhaustive than the one in the study guide.
- If you're looking to be really clever you can quote Michael Porter on 'what is added value?'. Michael Porter looks at this from a customer perspective - 'added value' refers to the addition of greater value (either by reducing the cost to produce it, or by adding something that customers are willing to pay more for). These could be; marketing / design, customer service, maintenance, delivery etc. This comes up at Level 5 / 6.
- Latest Upload
- 148Microsoft.SC-200.v2025-12-15.q150
- 125Fortinet.FCSS_EFW_AD-7.6.v2025-12-15.q26
- 135Microsoft.SC-300.v2025-12-15.q140
- 149Microsoft.MS-900.v2025-12-15.q191
- 135Avaya.78202T.v2025-12-14.q94
- 130EMC.D-PST-DY-23.v2025-12-14.q89
- 121HP.HPE0-S59.v2025-12-14.q35
- 132HP.HPE7-A08.v2025-12-13.q70
- 181DAMA.DMF-1220.v2025-12-13.q310
- 126SAP.C_ABAPD_2507.v2025-12-13.q33

