303 Exam Question 36
An TLM Specialist needs to configure a virtual server to terminate SSL connection on the LTM device.
Cryptographic information must be re-authorized for SSL sessions that remain open for longer than 30 seconds.
Which settings should the LTM Specialist configure in the client SSL profile?
Cryptographic information must be re-authorized for SSL sessions that remain open for longer than 30 seconds.
Which settings should the LTM Specialist configure in the client SSL profile?
303 Exam Question 37
An LTM device has a virtual server mapped to www.f5.com with a pool assigned. Users report that when browsing, they are periodically required to re-login to /resources/201.1.7.b.2_l.com. The objects are defined as follows:
Virtual server. Destination 192.168.245.100:443 netmask 255.255.255.0
Persistence: SSL session persistence
Profiles: HTTP/TCP
Which persistence method should the BIG-IP Administrator apply to resolve this issue?
Virtual server. Destination 192.168.245.100:443 netmask 255.255.255.0
Persistence: SSL session persistence
Profiles: HTTP/TCP
Which persistence method should the BIG-IP Administrator apply to resolve this issue?
303 Exam Question 38
A BIG-IP Administrator is performing maintenance on the active BIG-IP device of an HA pair. The BIG-IP Administrator needs to minimize traffic disruptions.
What should the BIG-IP Administrator do to start the maintenance activity?
What should the BIG-IP Administrator do to start the maintenance activity?
303 Exam Question 39
Refer to the exhibit.
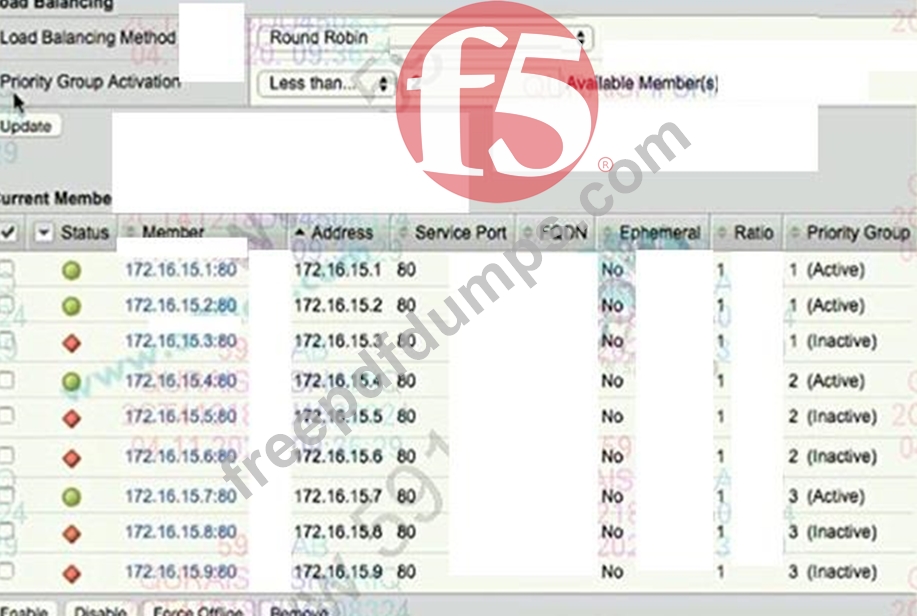
Which two pool members should be chosen for a new connection? (Choose two.)

Which two pool members should be chosen for a new connection? (Choose two.)
303 Exam Question 40
There are three servers in the pool: 172.16.20.1, 172.16.20.2, and 172.16.20.3, with the virtual IP address
10.0.20.88.
A user CANNOT connect to an HTTP application. To understand the problem and find a solution, the LTM Specialist runs two concurrent traces on the LTM device, with the following results:
Trace on client side:
tcpdump: verbose output suppressed, use -v or -vv for full protocol decode listening on 0.0, link-type EN10MB (Ethernet), capture size 96 bytes
22:22:07.423759 IP 172.16.20.100.53875 > 10.0.20.88.80: S 998346084:998346084(0) win 5840 <mss
1460,sackOK,timestamp 67942058 0,nop,wscale 4>
22:22:07.424056 IP 10.0.20.88.80 > 172.16.20.100.53875: S 4671780:4671780(0) ack 998346085 win 4380
<mss 1460,nop,wscale 0,nop,nop,timestamp 2392362490 67942058,sackOK,eol>
22:22:07.424776 IP 172.16.20.100.53875 > 10.0.20.88.80: . ack 1 win 365 <nop,nop,timestamp 67942058
2392362490>
22:22:07.424790 IP 172.16.20.100.53875 > 10.0.20.88.80: P 1:149(148) ack 1 win 365 <nop,nop,timestamp
67942058 2392362490>
22:22:07.424891 IP 10.0.20.88.80 > 172.16.20.100.53875: . ack 149 win 4528 <nop,nop,timestamp
2392362491 67942058>
22:22:12.024850 IP 10.0.20.88.80 > 172.16.20.100.53875: R 1:1(0) ack 149 win 4528
6 packets captured
6 packets received by filter
0 packets dropped by kernel
Trace on server side:
tcpdump: verbose output suppressed, use -v or -vv for full protocol decode listening on internal, link-type EN10MB (Ethernet), capture size 96 bytes
22:22:07.424881 IP 172.16.20.100.53875 > 172.16.20.2.80: S 51116678:51116678(0) win 4380 <mss
1460,nop,wscale 0,nop,nop,timestamp 2392362491 0,sackOK,eol>
22:22:08.424893 IP 172.16.20.100.53875 > 172.16.20.2.80: S 51116678:51116678(0) win 4380 <mss
1460,nop,wscale 0,nop,nop,timestamp 2392363491 0,sackOK,eol>
22:22:09.625082 IP 172.16.20.100.53875 > 172.16.20.2.80: S 51116678:51116678(0) win 4380 <mss
1460,nop,wscale 0,nop,nop,timestamp 2392364691 0,sackOK,eol>
22:22:10.825194 IP 172.16.20.100.53875 > 172.16.20.2.80: S 51116678:51116678(0) win 4380 <mss
1460,sackOK,eol>
4 packets captured
4 packets received by filter
0 packets dropped by kernel
What should the LTM Specialist do to solve the problem?
10.0.20.88.
A user CANNOT connect to an HTTP application. To understand the problem and find a solution, the LTM Specialist runs two concurrent traces on the LTM device, with the following results:
Trace on client side:
tcpdump: verbose output suppressed, use -v or -vv for full protocol decode listening on 0.0, link-type EN10MB (Ethernet), capture size 96 bytes
22:22:07.423759 IP 172.16.20.100.53875 > 10.0.20.88.80: S 998346084:998346084(0) win 5840 <mss
1460,sackOK,timestamp 67942058 0,nop,wscale 4>
22:22:07.424056 IP 10.0.20.88.80 > 172.16.20.100.53875: S 4671780:4671780(0) ack 998346085 win 4380
<mss 1460,nop,wscale 0,nop,nop,timestamp 2392362490 67942058,sackOK,eol>
22:22:07.424776 IP 172.16.20.100.53875 > 10.0.20.88.80: . ack 1 win 365 <nop,nop,timestamp 67942058
2392362490>
22:22:07.424790 IP 172.16.20.100.53875 > 10.0.20.88.80: P 1:149(148) ack 1 win 365 <nop,nop,timestamp
67942058 2392362490>
22:22:07.424891 IP 10.0.20.88.80 > 172.16.20.100.53875: . ack 149 win 4528 <nop,nop,timestamp
2392362491 67942058>
22:22:12.024850 IP 10.0.20.88.80 > 172.16.20.100.53875: R 1:1(0) ack 149 win 4528
6 packets captured
6 packets received by filter
0 packets dropped by kernel
Trace on server side:
tcpdump: verbose output suppressed, use -v or -vv for full protocol decode listening on internal, link-type EN10MB (Ethernet), capture size 96 bytes
22:22:07.424881 IP 172.16.20.100.53875 > 172.16.20.2.80: S 51116678:51116678(0) win 4380 <mss
1460,nop,wscale 0,nop,nop,timestamp 2392362491 0,sackOK,eol>
22:22:08.424893 IP 172.16.20.100.53875 > 172.16.20.2.80: S 51116678:51116678(0) win 4380 <mss
1460,nop,wscale 0,nop,nop,timestamp 2392363491 0,sackOK,eol>
22:22:09.625082 IP 172.16.20.100.53875 > 172.16.20.2.80: S 51116678:51116678(0) win 4380 <mss
1460,nop,wscale 0,nop,nop,timestamp 2392364691 0,sackOK,eol>
22:22:10.825194 IP 172.16.20.100.53875 > 172.16.20.2.80: S 51116678:51116678(0) win 4380 <mss
1460,sackOK,eol>
4 packets captured
4 packets received by filter
0 packets dropped by kernel
What should the LTM Specialist do to solve the problem?

