CKS Exam Question 6
SIMULATION
Create a Pod name Nginx-pod inside the namespace testing, Create a service for the Nginx-pod named nginx-svc, using the ingress of your choice, run the ingress on tls, secure port.
Create a Pod name Nginx-pod inside the namespace testing, Create a service for the Nginx-pod named nginx-svc, using the ingress of your choice, run the ingress on tls, secure port.
CKS Exam Question 7
SIMULATION
Using the runtime detection tool Falco, Analyse the container behavior for at least 30 seconds, using filters that detect newly spawning and executing processes store the incident file art /opt/falco-incident.txt, containing the detected incidents. one per line, in the format
[timestamp],[uid],[user-name],[processName]
Using the runtime detection tool Falco, Analyse the container behavior for at least 30 seconds, using filters that detect newly spawning and executing processes store the incident file art /opt/falco-incident.txt, containing the detected incidents. one per line, in the format
[timestamp],[uid],[user-name],[processName]
CKS Exam Question 8
Cluster: dev
Master node: master1
Worker node: worker1
You can switch the cluster/configuration context using the following command:
[desk@cli] $ kubectl config use-context dev
Task:
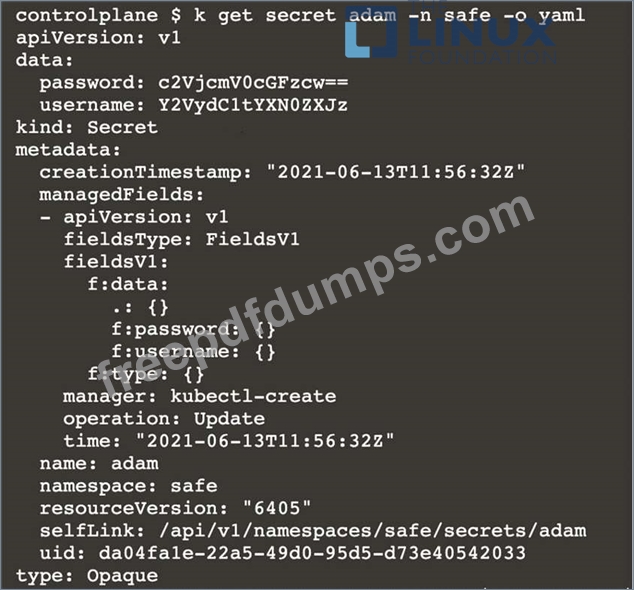
Retrieve the content of the existing secret named adam in the safe namespace.
Store the username field in a file names /home/cert-masters/username.txt, and the password field in a file named /home/cert-masters/password.txt.
1. You must create both files; they don't exist yet.
2. Do not use/modify the created files in the following steps, create new temporary files if needed.
Create a new secret names newsecret in the safe namespace, with the following content:
Username: dbadmin
Password: moresecurepas
Finally, create a new Pod that has access to the secret newsecret via a volume:
Namespace: safe
Pod name: mysecret-pod
Container name: db-container
Image: redis
Volume name: secret-vol
Mount path: /etc/mysecret
Master node: master1
Worker node: worker1
You can switch the cluster/configuration context using the following command:
[desk@cli] $ kubectl config use-context dev
Task:
Retrieve the content of the existing secret named adam in the safe namespace.
Store the username field in a file names /home/cert-masters/username.txt, and the password field in a file named /home/cert-masters/password.txt.
1. You must create both files; they don't exist yet.
2. Do not use/modify the created files in the following steps, create new temporary files if needed.
Create a new secret names newsecret in the safe namespace, with the following content:
Username: dbadmin
Password: moresecurepas
Finally, create a new Pod that has access to the secret newsecret via a volume:
Namespace: safe
Pod name: mysecret-pod
Container name: db-container
Image: redis
Volume name: secret-vol
Mount path: /etc/mysecret
CKS Exam Question 9
Cluster: admission-cluster
Master node: master
Worker node: worker1
You can switch the cluster/configuration context using the following command:
[desk@cli] $ kubectl config use-context admission-cluster
Context:
A container image scanner is set up on the cluster, but it's not yet fully integrated into the cluster's configuration. When complete, the container image scanner shall scan for and reject the use of vulnerable images.
Task:
You have to complete the entire task on the cluster's master node, where all services and files have been prepared and placed.
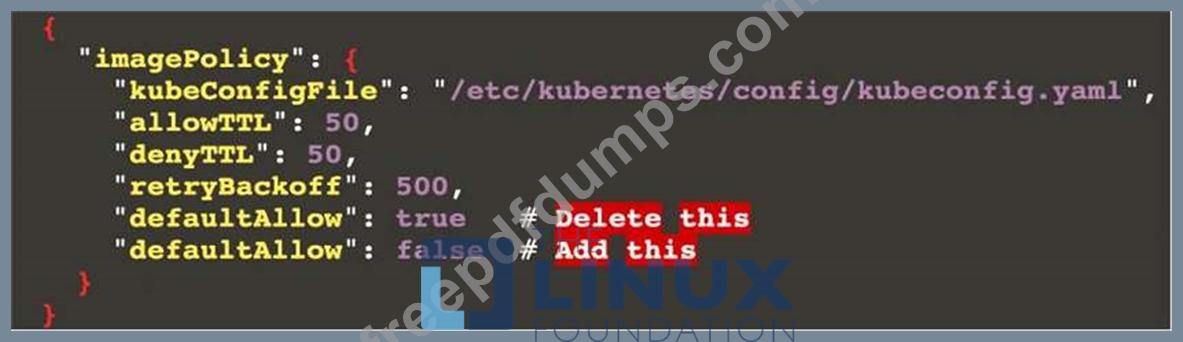
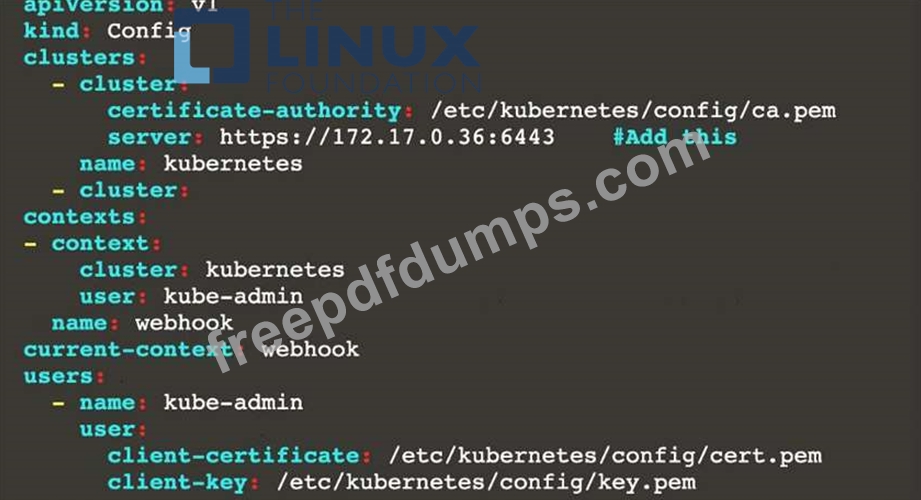
Given an incomplete configuration in directory /etc/Kubernetes/config and a functional container image scanner with HTTPS endpoint https://imagescanner.local:8181/image_policy:
1. Enable the necessary plugins to create an image policy
2. Validate the control configuration and change it to an implicit deny
3. Edit the configuration to point to the provided HTTPS endpoint correctly Finally, test if the configuration is working by trying to deploy the vulnerable resource /home/cert_masters/test-pod.yml Note: You can find the container image scanner's log file at /var/log/policy/scanner.log
Master node: master
Worker node: worker1
You can switch the cluster/configuration context using the following command:
[desk@cli] $ kubectl config use-context admission-cluster
Context:
A container image scanner is set up on the cluster, but it's not yet fully integrated into the cluster's configuration. When complete, the container image scanner shall scan for and reject the use of vulnerable images.
Task:
You have to complete the entire task on the cluster's master node, where all services and files have been prepared and placed.
Given an incomplete configuration in directory /etc/Kubernetes/config and a functional container image scanner with HTTPS endpoint https://imagescanner.local:8181/image_policy:
1. Enable the necessary plugins to create an image policy
2. Validate the control configuration and change it to an implicit deny
3. Edit the configuration to point to the provided HTTPS endpoint correctly Finally, test if the configuration is working by trying to deploy the vulnerable resource /home/cert_masters/test-pod.yml Note: You can find the container image scanner's log file at /var/log/policy/scanner.log
CKS Exam Question 10
You can switch the cluster/configuration context using the following command:
[desk@cli] $ kubectl config use-context test-account
Task: Enable audit logs in the cluster.
To do so, enable the log backend, and ensure that:
1. logs are stored at /var/log/Kubernetes/logs.txt
2. log files are retained for 5 days
3. at maximum, a number of 10 old audit log files are retained
A basic policy is provided at /etc/Kubernetes/logpolicy/audit-policy.yaml. It only specifies what not to log.
Note: The base policy is located on the cluster's master node.
Edit and extend the basic policy to log:
1. Nodes changes at RequestResponse level
2. The request body of persistentvolumes changes in the namespace frontend
3. ConfigMap and Secret changes in all namespaces at the Metadata level Also, add a catch-all rule to log all other requests at the Metadata level Note: Don't forget to apply the modified policy.
[desk@cli] $ kubectl config use-context test-account
Task: Enable audit logs in the cluster.
To do so, enable the log backend, and ensure that:
1. logs are stored at /var/log/Kubernetes/logs.txt
2. log files are retained for 5 days
3. at maximum, a number of 10 old audit log files are retained
A basic policy is provided at /etc/Kubernetes/logpolicy/audit-policy.yaml. It only specifies what not to log.
Note: The base policy is located on the cluster's master node.
Edit and extend the basic policy to log:
1. Nodes changes at RequestResponse level
2. The request body of persistentvolumes changes in the namespace frontend
3. ConfigMap and Secret changes in all namespaces at the Metadata level Also, add a catch-all rule to log all other requests at the Metadata level Note: Don't forget to apply the modified policy.